by urban-acupuncture | Feb 5, 2025 | Electroacupuncture
Electroacupuncture Improved Motor Dysfunction and Constipation
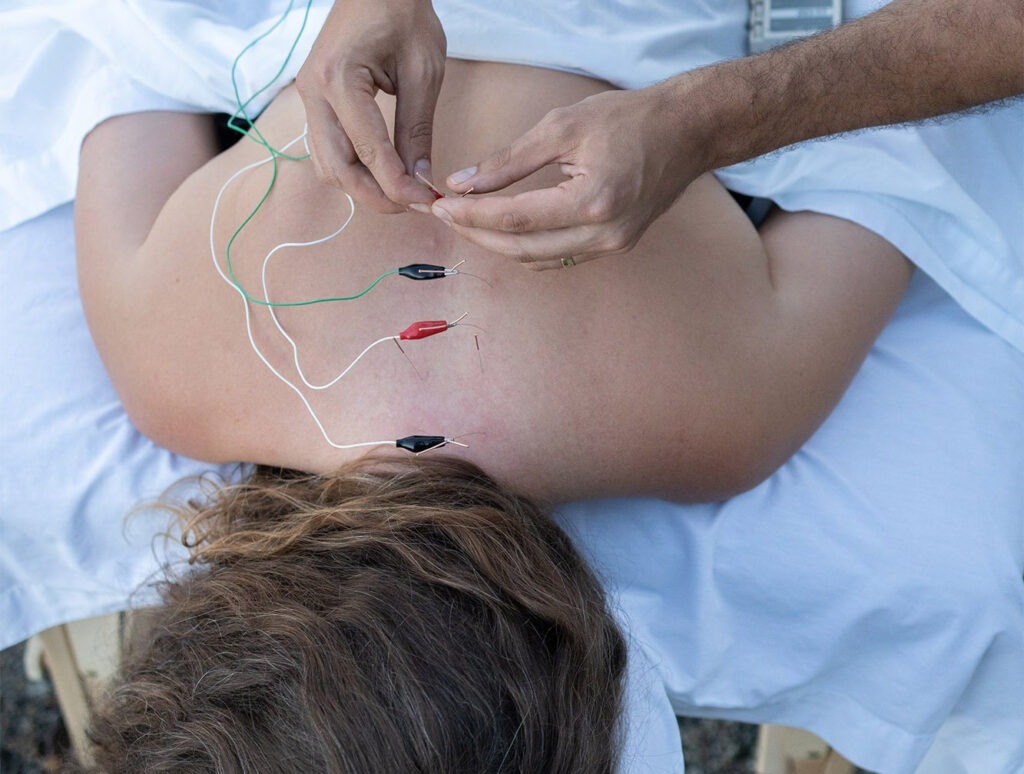 Parkinson’s disease (PD), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, is characterized by motor dysfunctions such as tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability, as well as non-motor symptoms like constipation. While dopaminergic medications have been the cornerstone of PD treatment, their effectiveness tends to diminish over time, and they are often accompanied by undesirable side effects. Consequently, alternative treatments such as electroacupuncture have garnered increasing attention for their potential to alleviate symptoms, particularly in patients with motor dysfunction and constipation. A recent randomized controlled multi-centre trial provides compelling evidence on the efficacy of electroacupuncture in managing these common PD symptoms.
Parkinson’s disease (PD), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, is characterized by motor dysfunctions such as tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability, as well as non-motor symptoms like constipation. While dopaminergic medications have been the cornerstone of PD treatment, their effectiveness tends to diminish over time, and they are often accompanied by undesirable side effects. Consequently, alternative treatments such as electroacupuncture have garnered increasing attention for their potential to alleviate symptoms, particularly in patients with motor dysfunction and constipation. A recent randomized controlled multi-centre trial provides compelling evidence on the efficacy of electroacupuncture in managing these common PD symptoms.
Study Overview
The study aimed to assess the impact of electroacupuncture on motor dysfunction and constipation in PD patients. Conducted across multiple centres, the trial randomized patients into two groups: one group received electroacupuncture treatment, while the other was given a placebo treatment. Over a period of 12 weeks, the study evaluated changes in motor function, as well as the frequency and severity of constipation symptoms.
Methods
The study involved a total of 150 participants diagnosed with PD, all of whom exhibited significant motor dysfunction and constipation. Electroacupuncture was administered by skilled practitioners, targeting specific acupoints traditionally used to enhance motor function and relieve gastrointestinal issues. The intervention consisted of 20-minute sessions, three times per week, for 12 weeks.
The primary outcomes of the trial were improvements in motor function, measured using the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS), and improvements in constipation, assessed using the Cleveland Clinic Constipation Score (CCCS). Secondary outcomes included changes in quality of life and adverse events.
Results: Electroacupuncture Led to Significant Improvements in Motor Function
The results of the study demonstrated that electroacupuncture led to significant improvements in both motor function and constipation when compared to the placebo group. Specifically, patients receiving electroacupuncture showed a notable reduction in UPDRS scores, reflecting improvements in motor performance. Furthermore, these patients reported significant relief from constipation symptoms, evidenced by decreased CCCS scores.
Notably, the benefits of electroacupuncture were sustained over the 12-week treatment period, and the treatment was generally well-tolerated with minimal adverse effects. The placebo group, on the other hand, showed no significant improvements in either motor function or constipation.
Discussion
The results from this multi-centre trial add to a growing body of evidence suggesting that electroacupuncture may be an effective complementary therapy for managing both motor and non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. The mechanisms underlying these improvements are not entirely understood, but it is hypothesized that electroacupuncture may help modulate the autonomic nervous system and restore the balance of neurotransmitters involved in motor control and gastrointestinal function.
The study also underscores the potential of electroacupuncture as a safe and non-invasive treatment option for PD patients who may not respond adequately to pharmacological treatments or those who experience undesirable side effects from conventional therapies.
This randomized controlled trial provides stronger evidence supporting the use of electroacupuncture for the treatment of motor dysfunction and constipation in patients with Parkinson’s disease.
The significant improvements observed in both motor symptoms and gastrointestinal function suggest that electroacupuncture can be a valuable adjunct to conventional treatments for PD, particularly in patients seeking alternative therapies. Given its safety profile and minimal adverse effects, electroacupuncture should be further explored in larger-scale trials to better understand its long-term efficacy and potential for widespread clinical use.
For a more detailed review of the study, refer to the full article available here.
Contact Urban Acupuncture Center in Columbus, OH For More Information
For more information about how acupuncture, massage therapy, electroacupuncture and other alternative healing treatments can help you, please contact the Urban Acupuncture Center Board Certified Licensed Acupuncturist’s team at Indianola Ave, Columbus, Ohio (Clintonville) (614) 725-2488 or click here. Taking new patients in and around greater Columbus, Ohio.
by urban-acupuncture | Feb 1, 2025 | Electroacupuncture
Insomnia Treatment
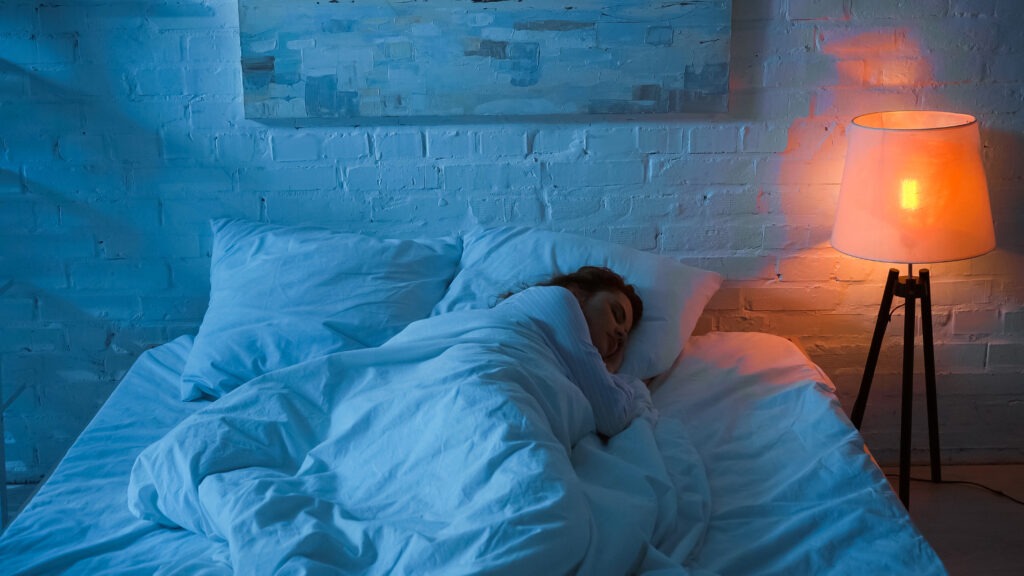

Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, leading to difficulties falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early. Chronic insomnia can negatively impact overall health, mood, and cognitive function. While traditional treatments like medications and cognitive behavioral therapy are commonly prescribed, many people seek alternative or complementary therapies to manage their symptoms. One such treatment gaining attention is electroacupuncture. This technique combines traditional acupuncture with electrical stimulation and has shown promise in improving sleep architecture and increasing deep sleep time in individuals with insomnia. In this article, we’ll explore how electroacupuncture works and how it can help improve sleep quality for those struggling with insomnia.
What is Electroacupuncture?
Electroacupuncture is a modern variation of traditional acupuncture. It involves the use of small electrical currents applied to acupuncture needles placed at specific points along the body’s energy channels, or meridians. The electrical stimulation enhances the effects of acupuncture by promoting deeper penetration of the treatment and potentially increasing the therapeutic benefits. Unlike traditional acupuncture, which relies solely on needle insertion, electroacupuncture adds a gentle electrical current to stimulate the points more effectively.
Acupuncture itself has been used for thousands of years in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) to balance the body’s energy, promote healing, and address various ailments. Electroacupuncture takes this ancient practice a step further by using electrical stimulation to amplify its effects, making it a powerful tool for treating modern health conditions like insomnia.
Understanding Sleep Architecture and Deep Sleep
To understand how electroacupuncture can improve sleep, it’s important to first know about sleep architecture. Sleep architecture refers to the structure of sleep cycles, including the different stages of sleep we experience throughout the night:
- Stage 1 (Light Sleep): The transition from wakefulness to sleep. It is a short, light phase where muscle activity and heart rate slow down.
- Stage 2 (Light Sleep): Deeper than stage 1, but still not considered restorative. The body temperature drops, and heart rate continues to slow.
- Stage 3 and 4 (Deep Sleep): Often referred to as slow-wave sleep (SWS), these stages are critical for physical restoration, tissue repair, immune function, and memory consolidation. Deep sleep is the most restorative phase of sleep.
- REM Sleep (Rapid Eye Movement): This stage is associated with vivid dreaming and brain activity similar to wakefulness. REM sleep plays a significant role in cognitive functions like memory, learning, and emotional regulation.
People with insomnia often experience disruptions in their sleep architecture, such as reduced deep sleep or REM sleep, and prolonged periods of light sleep. These disruptions prevent the body from fully restoring itself during sleep, leading to daytime fatigue, mood disturbances, and decreased cognitive performance.
How Electroacupuncture Can Improve Sleep Architecture
Electroacupuncture may help improve sleep architecture in people with insomnia by:
- Increasing Deep Sleep Time One of the most significant benefits of electroacupuncture for people with insomnia is its ability to increase the amount of deep sleep (stage 3 and 4). Deep sleep is vital for physical restoration and immune system functioning, and it is often lacking in people with insomnia. Research suggests that electroacupuncture can help enhance the production of slow-wave sleep, allowing for longer periods of deep sleep. This is likely due to the stimulation of specific acupuncture points that regulate the nervous system, promote relaxation, and balance sleep-wake cycles.
- Balancing the Sleep-Wake Cycle Electroacupuncture is believed to influence the hypothalamus, a part of the brain that regulates sleep, body temperature, and hormone secretion. By modulating hypothalamic activity, electroacupuncture may help restore balance to the circadian rhythm (the body’s internal clock) and promote a more consistent sleep-wake cycle. As a result, individuals may find it easier to fall asleep, stay asleep, and experience more restorative sleep throughout the night.
- Promoting Relaxation and Reducing Stress Stress is a common trigger for insomnia, and many individuals with sleep problems experience an overactive sympathetic nervous system (the fight-or-flight response). Electroacupuncture helps stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for promoting relaxation and rest. The electrical stimulation of acupuncture points can help reduce cortisol levels (the stress hormone), ease muscle tension, and activate the body’s relaxation response. This leads to an improved ability to wind down and enter deeper stages of sleep.
- Increasing Melatonin Production Melatonin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating sleep-wake cycles. Electroacupuncture may help enhance melatonin production by stimulating specific acupuncture points. Studies have shown that acupuncture and electroacupuncture can increase melatonin levels, potentially helping individuals with insomnia fall asleep more easily and enjoy better sleep quality. Higher melatonin levels are associated with both improved sleep onset and prolonged deep sleep.
- Improving Overall Sleep Quality In addition to increasing deep sleep, electroacupuncture may also improve overall sleep quality. This means that individuals may experience fewer awakenings during the night, more time spent in restorative sleep stages, and reduced sleep fragmentation. The cumulative effects of improved deep sleep, better sleep continuity, and reduced anxiety contribute to a more restful and rejuvenating night of sleep.
Evidence Supporting Electroacupuncture for Insomnia
Several studies have explored the effects of electroacupuncture on sleep disorders, particularly insomnia. Research has shown that electroacupuncture can significantly improve sleep quality by increasing deep sleep time, reducing sleep onset latency (the time it takes to fall asleep), and decreasing nighttime awakenings. For example, a study published in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine found that electroacupuncture was effective in improving sleep quality and duration in patients with primary insomnia. Participants reported feeling more refreshed and rested after treatment.
Another study in the Journal of Sleep Research demonstrated that electroacupuncture helped reduce the frequency of awakenings and prolonged deep sleep in patients with insomnia. These studies highlight the potential of electroacupuncture as a viable treatment for improving sleep architecture in individuals with sleep disturbances.
Is Electroacupuncture Safe for Insomnia?
Electroacupuncture is generally considered safe when performed by a trained practitioner. It is a non-invasive therapy that does not involve the use of medications, which makes it an attractive option for individuals who prefer natural treatments. However, as with any treatment, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting electroacupuncture, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medication.
Electroacupuncture offers a promising approach to improving sleep quality for people with insomnia by enhancing sleep architecture, increasing deep sleep time, and promoting relaxation.
By addressing the underlying causes of sleep disturbances and restoring balance to the sleep-wake cycle, electroacupuncture provides a holistic treatment option for those seeking relief from insomnia. As a non-invasive and drug-free therapy, electroacupuncture may be an effective complementary treatment for those struggling with sleep disorders and looking for an alternative to traditional medications.
Contact Urban Acupuncture Center in Columbus, OH For More Information
For more information about how acupuncture, massage therapy, electroacupuncture and other alternative healing treatments can help you, please contact the Urban Acupuncture Center Board Certified Licensed Acupuncturist’s team at Indianola Ave, Columbus, Ohio (Clintonville) (614) 725-2488 or click here. Taking new patients in and around greater Columbus, Ohio.
by urban-acupuncture | Jan 30, 2025 | Acupuncture
 Aging is inevitable. We start aging the day we’re born. Aging isn’t just about how we look, it’s about how we feel.
Aging is inevitable. We start aging the day we’re born. Aging isn’t just about how we look, it’s about how we feel.
Acupuncture can improve longevity, vitality, quality of life, and restore our energy flow. Not only can it help us live longer, it can make the process more enjoyable.
Regular acupuncture (and for that matter, any modality that helps maintain your health including reiki, cupping, massage, bodywork, reflexology, exercise, stretching, etc) can reduce stress, increase circulation, decrease puffiness, improve hormonal balance, regulate oxidative stress, promote healing after surgery, and decrease inflammation and pain.
Acupuncture, along with other health modalities, can significantly extend the quality of life you experience as you age. Even if you are fortunate enough to age with minimal pain or chronic conditions, regular monthly or bi-monthly acupuncture treatments can help maintain the status quo.
Taking care of yourself is critical to longevity. This means taking care of your WHOLE self. Feed your spiritual, mental, social, and physical body as best you can to keep it steady, grounded, and as pain free as possible. If you haven’t tried reflexology, cupping, GuaSha, reiki, Trager, deep-tissue massage or structural bodywork yet, maybe now is the time. We look forward to seeing you soon!
Contact Urban Acupuncture Center in Columbus, OH For More Information
For more information about how acupuncture, massage therapy, electroacupuncture and other alternative healing treatments can help you, please contact the Urban Acupuncture Center Board Certified Licensed Acupuncturist’s team at Indianola Ave, Columbus, Ohio (Clintonville) (614) 725-2488 or click here. Taking new patients in and around greater Columbus, Ohio.
by urban-acupuncture | Jan 10, 2025 | Electroacupuncture
Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting Treatment
 Chemotherapy is a powerful treatment for cancer, but it often comes with challenging side effects, one of the most common and distressing of which is nausea and vomiting. While medications are available to help manage these symptoms, they aren’t always effective for everyone. This has led many patients and healthcare providers to explore complementary therapies like electroacupuncture as an alternative or adjunctive treatment. Electroacupuncture, a modern version of traditional acupuncture that adds a gentle electrical current to enhance therapeutic effects, shows promise in reducing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV), offering a more holistic approach to supportive cancer care.
Chemotherapy is a powerful treatment for cancer, but it often comes with challenging side effects, one of the most common and distressing of which is nausea and vomiting. While medications are available to help manage these symptoms, they aren’t always effective for everyone. This has led many patients and healthcare providers to explore complementary therapies like electroacupuncture as an alternative or adjunctive treatment. Electroacupuncture, a modern version of traditional acupuncture that adds a gentle electrical current to enhance therapeutic effects, shows promise in reducing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV), offering a more holistic approach to supportive cancer care.
Understanding Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting (CINV)
Chemotherapy drugs are powerful agents designed to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells, but in the process, they can also irritate the gastrointestinal system and stimulate the brain’s vomiting center. CINV can be divided into different types based on when symptoms appear:
- Acute nausea and vomiting occurs within 24 hours of chemotherapy.
- Delayed nausea and vomiting may occur several days after chemotherapy.
- Anticipatory nausea and vomiting happens before chemotherapy, triggered by psychological association with previous sessions.
Medications called antiemetics are often used to control CINV, but some patients still experience symptoms despite treatment, and others may seek non-drug solutions due to side effects or personal preferences. Electroacupuncture provides a promising alternative or complementary therapy to help manage these challenging symptoms.
What Is Electroacupuncture?
Electroacupuncture is a modern adaptation of traditional acupuncture, which involves inserting fine, sterile needles into specific points on the body. Electroacupuncture goes a step further by delivering a mild electrical current through the needles. The current is adjustable and can be tailored to each patient’s tolerance and therapeutic needs. This enhancement of traditional acupuncture techniques is thought to increase its effectiveness, particularly for pain management, nausea, and vomiting.
Studies show that the combination of traditional acupuncture with electrical stimulation enhances the effects on nerve pathways, endorphin release, and blood flow. For chemotherapy patients, this translates to potential relief from nausea, reduced vomiting, and overall improved comfort.
How Electroacupuncture May Help Relieve CINV
- Regulates Digestive Function: Electroacupuncture is known to stimulate the vagus nerve, which plays a key role in regulating the digestive system. By stimulating this nerve, electroacupuncture may help control nausea and reduce the frequency of vomiting. This effect can make a significant difference in helping patients maintain their appetite and hydration during chemotherapy.
- Increases Endorphin and Serotonin Release: Studies suggest that electroacupuncture can stimulate the body to release endorphins and serotonin—natural pain-relieving and mood-enhancing chemicals. This increase in serotonin is particularly important because it helps regulate the brain’s vomiting center, reducing nausea and making it easier for patients to tolerate chemotherapy.
- Balances Autonomic Nervous System: Chemotherapy often disrupts the balance of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which controls involuntary functions like digestion and heart rate. Electroacupuncture can help restore balance to the ANS, promoting relaxation and alleviating nausea. The calming effect of electroacupuncture may also reduce anticipatory nausea, helping patients feel less anxious about their treatments.
- Reduces Inflammation: Chemotherapy can induce inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, which may contribute to nausea. Electroacupuncture has shown anti-inflammatory effects, helping to alleviate gastrointestinal irritation and reduce the likelihood of nausea and vomiting.
- Promotes Better Sleep and Reduces Stress: Electroacupuncture’s calming effect on the nervous system can improve sleep quality and reduce stress. Since fatigue and stress can exacerbate nausea, this additional benefit can help patients feel more comfortable and better equipped to manage chemotherapy.
Electroacupuncture vs. Traditional Acupuncture for CINV
Traditional acupuncture has been widely studied and used to help manage nausea and vomiting in cancer patients. Electroacupuncture builds upon these principles, adding electrical stimulation to enhance effects, particularly in cases where nausea is difficult to control. Research suggests that electroacupuncture can be more effective in reducing nausea intensity and frequency compared to traditional acupuncture alone, especially for those experiencing persistent CINV.
A study published in Oncology found that patients who received electroacupuncture during chemotherapy reported less severe nausea and fewer episodes of vomiting than those who received traditional acupuncture alone. Another study in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management indicated that patients who received electroacupuncture experienced faster relief and required fewer anti-nausea medications.
What to Expect During Electroacupuncture for CINV
If you’re considering electroacupuncture for chemotherapy-induced nausea, here’s what a typical session might involve:
- Consultation with a Licensed Acupuncturist: Your practitioner will discuss your health history, cancer treatment, and specific symptoms. They will assess your individual needs and choose appropriate acupuncture points for treatment.
- Application of Needles: Thin, sterile needles will be inserted into specific points, often on the wrist, forearm, and lower leg, which correspond to areas associated with nausea relief and digestive support.
- Electrical Stimulation: Once the needles are placed, the practitioner will connect a small electrical device to the needles, delivering a controlled current. The sensation is usually described as a mild tingling, which should not be painful or uncomfortable.
- Relaxation and Monitoring: The session typically lasts about 20-30 minutes. You may feel deeply relaxed during and after treatment, as electroacupuncture helps relieve stress and tension.
- Aftercare and Follow-Up: Depending on the severity of CINV, you may need several sessions over a few weeks. Many patients experience relief after the first few treatments, while others benefit from ongoing sessions to manage symptoms throughout chemotherapy.
Evidence Supporting Electroacupuncture for CINV
Several clinical studies support the effectiveness of electroacupuncture for managing CINV:
- A study published in Supportive Care in Cancer found that electroacupuncture significantly reduced nausea and vomiting in chemotherapy patients compared to traditional antiemetic medications alone. Patients reported greater comfort and better appetite after electroacupuncture sessions.
- Research from the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine demonstrated that electroacupuncture at specific acupuncture points helped reduce both acute and delayed nausea, suggesting its utility throughout different stages of CINV.
- In another trial, cancer patients who received electroacupuncture reported not only reduced nausea but also improved overall quality of life, including better sleep and mood.
Safety Considerations and Potential Side Effects
Electroacupuncture is generally safe when performed by a licensed and experienced acupuncturist. However, patients with certain medical conditions, such as pacemakers or electrical implants, should consult their doctor before undergoing electroacupuncture, as the electrical currents could interfere with these devices. As with any acupuncture treatment, some people may experience minor side effects, such as mild bruising, soreness, or fatigue following the session, though these effects are typically short-lived.
Integrating Electroacupuncture into a Comprehensive Treatment Plan
Electroacupuncture can be an effective complementary therapy for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, but it’s most beneficial when integrated into a comprehensive treatment plan. Patients should continue to use prescribed anti-nausea medications as directed by their oncologist, with electroacupuncture serving as an additional supportive therapy. This approach helps maximize symptom relief while minimizing the need for additional medications.
Electroacupuncture offers a promising, non-pharmacological option for managing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
By promoting natural pain relief, balancing the nervous system, and reducing inflammation, electroacupuncture provides cancer patients with a holistic method to cope with one of chemotherapy’s most challenging side effects. With its ability to enhance quality of life and relieve discomfort, electroacupuncture may be a valuable addition to cancer care, helping patients feel more comfortable and resilient throughout their treatment journey. As with any complementary therapy, it’s essential to consult with both your oncologist and a licensed acupuncturist to determine if electroacupuncture is right for you.
Contact Urban Acupuncture Center in Columbus, OH For More Information
For more information about how acupuncture, massage therapy, electroacupuncture and other alternative healing treatments can help you, please contact the Urban Acupuncture Center Board Certified Licensed Acupuncturist’s team at Indianola Ave, Columbus, Ohio (Clintonville) (614) 725-2488 or click here. Taking new patients in and around greater Columbus, Ohio.
by urban-acupuncture | Jan 9, 2025 | Holistic Health
Join Raj for a FULL MOON Gong bath this Sunday, January 12th @ 2:00 p.m. She will also offer gong baths on Sunday, February 9th & Sunday, March 16th. Sign up under classes or call the office.
She will also offer gong baths on Sunday, February 9th & Sunday, March 16th. Sign up under classes or call the office.
A full moon gong bath is a unique and deeply meditative sound healing experience that uses the vibrational energy of gongs, often aligned with the powerful energy of a full moon. Participants are “bathed” in sound waves, allowing their bodies, minds, and spirits to relax, heal, and reset. It is a holistic practice rooted in ancient traditions but has gained popularity in modern wellness practices for its profound physical and emotional benefits.
What Happens During a Full Moon Gong Bath?
- Preparation and Setting:
- The session typically begins with participants lying on mats or seated comfortably. They are encouraged to relax, close their eyes, and focus on their breath.
- The space is often dimly lit, with candles or crystals used to enhance the ambiance.
- The Gong’s Vibrations:
- A gong master plays one or multiple gongs, producing resonant tones and sound vibrations. These sounds range from deep, grounding tones to high, ethereal pitches.
- The sound waves penetrate deeply, creating a physical sensation that many describe as soothing or transformative.
- The Full Moon Connection:
- The full moon is believed to amplify the effects of the gong bath. Traditionally associated with heightened energy, intuition, and emotional release, the full moon adds an extra layer of potency to the experience.
- Practitioners may incorporate themes of letting go, setting intentions, or connecting with cosmic cycles.
What Does a Gong Bath Do?
- Physical Benefits:
- Stress Reduction: The deep vibrations of the gong stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
- Improved Sleep: Many participants report better sleep after a session due to the calming effects on the body and mind.
- Pain Relief: Sound waves can help release muscle tension and improve circulation, reducing physical discomfort.
- Emotional Benefits:
- Emotional Release: The vibrations can bring suppressed emotions to the surface, facilitating catharsis and emotional healing.
- Clarity and Balance: The gong bath helps quiet the mind, providing clarity and a sense of inner balance.
- Spiritual Benefits:
- Energy Alignment: The sound frequencies help balance chakras and realign your body’s energy.
- Connection to the Universe: The full moon adds a spiritual dimension, fostering a sense of connection to larger cosmic rhythms.
Who Can Benefit from a Full Moon Gong Bath?
- Stressed Individuals:
Anyone dealing with high levels of stress or anxiety can benefit from the relaxation and grounding effects.
- People Seeking Emotional Healing:
Those looking to release emotional blockages or gain clarity in their lives often find the gong bath transformative.
- Spiritual Seekers:
For individuals exploring spirituality, the full moon’s energy combined with the gong’s vibrations can deepen meditation and foster a sense of universal connection.
- Insomniacs:
The calming effects of a gong bath are particularly beneficial for those struggling with sleep issues.
- Creative Thinkers:
Artists, writers, and other creatives may find that the meditative state induced by a gong bath inspires new ideas and fresh perspectives.
How to Prepare for a Full Moon Gong Bath
- Wear Comfortable Clothing: Loose, breathable fabrics will help you fully relax.
- Bring Essentials: A yoga mat, blanket, and pillow will ensure you’re comfortable throughout the session.
- Set Intentions: Reflect on what you’d like to release or invite into your life during the experience.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink water before and after to support your body’s natural detoxification process.
A full moon gong bath is more than just a relaxing experience; it’s a holistic journey that nurtures the body, mind, and spirit. Whether you’re seeking stress relief, emotional healing, or a deeper connection to the universe, this ancient practice offers profound benefits that resonate on multiple levels.
Contact Urban Acupuncture Center in Columbus, OH For More Information
For more information about how acupuncture, massage therapy, electroacupuncture and other alternative healing treatments can help you, please contact the Urban Acupuncture Center Board Certified Licensed Acupuncturist’s team at Indianola Ave, Columbus, Ohio (Clintonville) (614) 725-2488 or click here. Taking new patients in and around greater Columbus, Ohio.
 Parkinson’s disease (PD), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, is characterized by motor dysfunctions such as tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability, as well as non-motor symptoms like constipation. While dopaminergic medications have been the cornerstone of PD treatment, their effectiveness tends to diminish over time, and they are often accompanied by undesirable side effects. Consequently, alternative treatments such as electroacupuncture have garnered increasing attention for their potential to alleviate symptoms, particularly in patients with motor dysfunction and constipation. A recent randomized controlled multi-centre trial provides compelling evidence on the efficacy of electroacupuncture in managing these common PD symptoms.
Parkinson’s disease (PD), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, is characterized by motor dysfunctions such as tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability, as well as non-motor symptoms like constipation. While dopaminergic medications have been the cornerstone of PD treatment, their effectiveness tends to diminish over time, and they are often accompanied by undesirable side effects. Consequently, alternative treatments such as electroacupuncture have garnered increasing attention for their potential to alleviate symptoms, particularly in patients with motor dysfunction and constipation. A recent randomized controlled multi-centre trial provides compelling evidence on the efficacy of electroacupuncture in managing these common PD symptoms.

 Aging is inevitable. We start aging the day we’re born. Aging isn’t just about how we look, it’s about how we feel.
Aging is inevitable. We start aging the day we’re born. Aging isn’t just about how we look, it’s about how we feel. Chemotherapy is a powerful treatment for cancer, but it often comes with challenging side effects, one of the most common and distressing of which is nausea and vomiting. While medications are available to help manage these symptoms, they aren’t always effective for everyone. This has led many patients and healthcare providers to explore complementary therapies like electroacupuncture as an alternative or adjunctive treatment. Electroacupuncture, a modern version of traditional acupuncture that adds a gentle electrical current to enhance therapeutic effects, shows promise in reducing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV), offering a more holistic approach to supportive cancer care.
Chemotherapy is a powerful treatment for cancer, but it often comes with challenging side effects, one of the most common and distressing of which is nausea and vomiting. While medications are available to help manage these symptoms, they aren’t always effective for everyone. This has led many patients and healthcare providers to explore complementary therapies like electroacupuncture as an alternative or adjunctive treatment. Electroacupuncture, a modern version of traditional acupuncture that adds a gentle electrical current to enhance therapeutic effects, shows promise in reducing chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV), offering a more holistic approach to supportive cancer care. She will also offer gong baths on Sunday, February 9th & Sunday, March 16th. Sign up under classes or call the office.
She will also offer gong baths on Sunday, February 9th & Sunday, March 16th. Sign up under classes or call the office.